Encription and Public Keys
Encription
What is Encryption
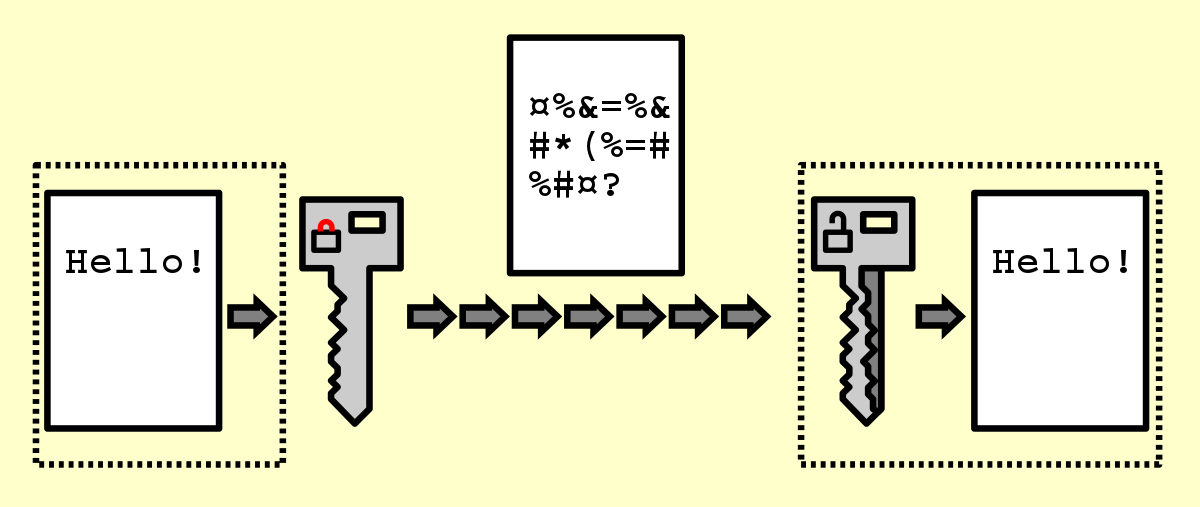
Encryption is the process of scrambling or enciphering data so it can be read only by someone with the means to return it to its original state. It is a crucial feature of a safe and trustworthy Internet. It helps provide data security for sensitive information.
Function
Encryption is commonly used to protect data stored on computer systems and data transmitted via computer networks, including the Internet. Financial transactions and private messaging communications often use encryption to increase security. Encryption is important when we need to find out whether data has been tampered with (data integrity), to increase people’s confidence that they are communicating with the people they think are communicating with (authentication) and to be sure that messages were sent and received (non-repudiation).
How Encryption Works ?
For data communicated over a network, encryption scrambles data using a secret value or key known only by the recipient and the sender. For stored data, the secret value is typically known only by the data owner.
Encryption Public Keys
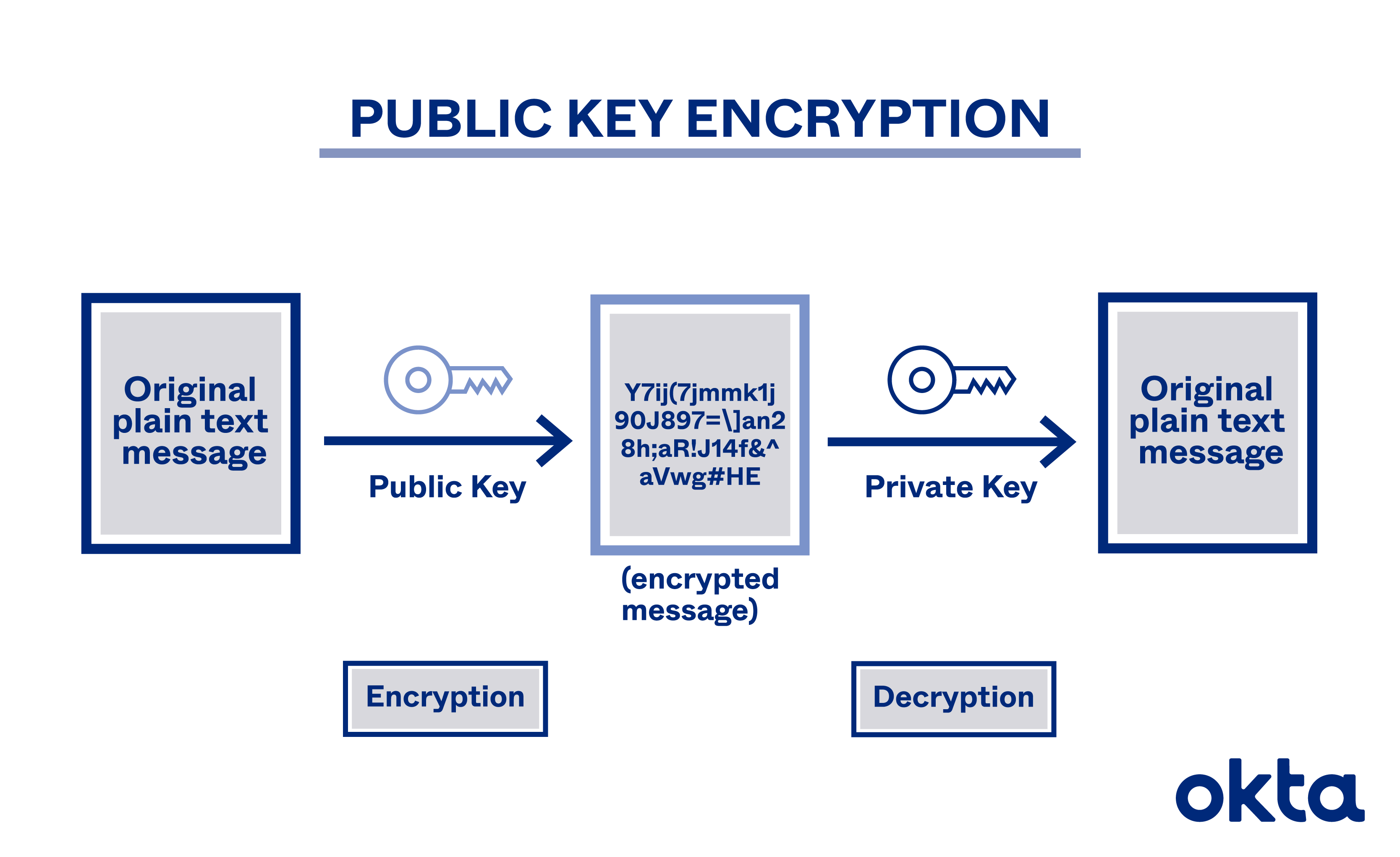
What is Encryption Public Key?
It is a method of encrypting data with 2 different keys, in which 1 key called Public Key is available for users to use and 1 key is Private Key. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa. Public key encryption also known as asymmetric encryption, is widely used for TLS/SSL(Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer).
Functions
Public key encryption is important because users can only decrypt encrypted data if they have the private key.
Either of the two keys, the public key and the private key, can be used for encryption with the key used for decryption.
In a public encryption system, public keys can be freely shared with users to encrypt data and verify digital signatures. Only the user who owns the private key can decrypt the encrypted data and create a digital signature.