Packets, Routing, and Reliability
Packets
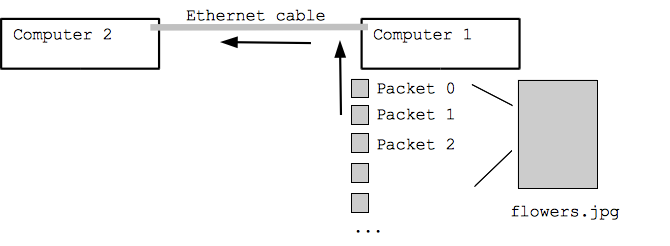 Packet is a term first coined by Donald Davies in 1965.
It is used to describe a segment of data that is sent from one computer or device to another
over a network.In simpler words, you can think of it as a packet full of data that is being
transferred to another region.
Packet is a term first coined by Donald Davies in 1965.
It is used to describe a segment of data that is sent from one computer or device to another
over a network.In simpler words, you can think of it as a packet full of data that is being
transferred to another region.
Packages divide data into more manageable “parts,” which move information more efficiently, and keep network resources from being constrained by a larger file.
A packet contains source, destination, data, size, and other useful information that helps
the packet to arrive at the proper location and reassemble properly.
Routing
Router
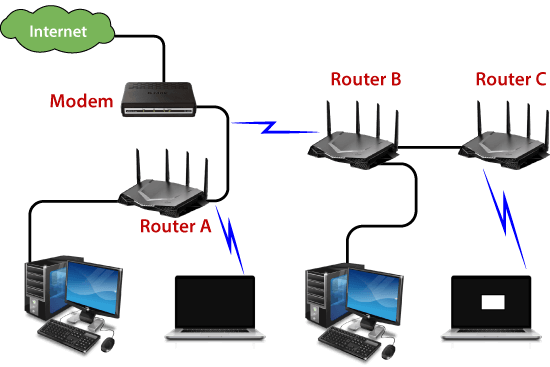
Router is a network device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Understandably, the router performs “direction of traffic” on the Internet.Data is sent on the Internet in the form of packets (Ex: email, web,…) , data packets will be forwarded from one router to another through small networks, which are connected to each other to form a network link, until the data packet reaches its destination.
In simple terms, routers connect devices in a network by transferring data packets between them. Routers perform this task by assigning a local IP address to each device on the network. This ensures that the data packet arrives at the right place and does not get lost in the network.
Routing
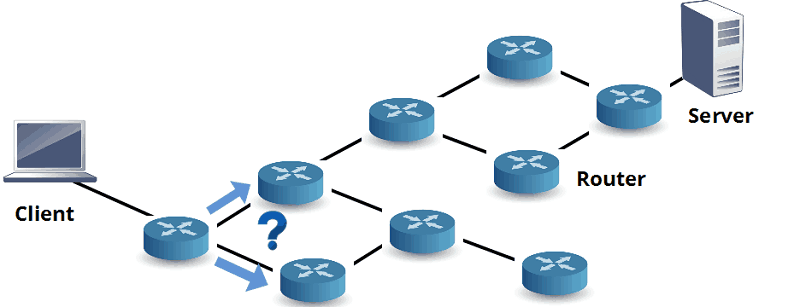
Routing is the method that a router or network device uses to deliver packets to the destination in the most optimal way, that is, to indicate the best direction and route for the packet. Routers collect and maintain routing information to enable transmission and reception of data.