Internet Overview
What is the internet?
The internet is global network of interconnected computing devices to communicate and share information with each other.
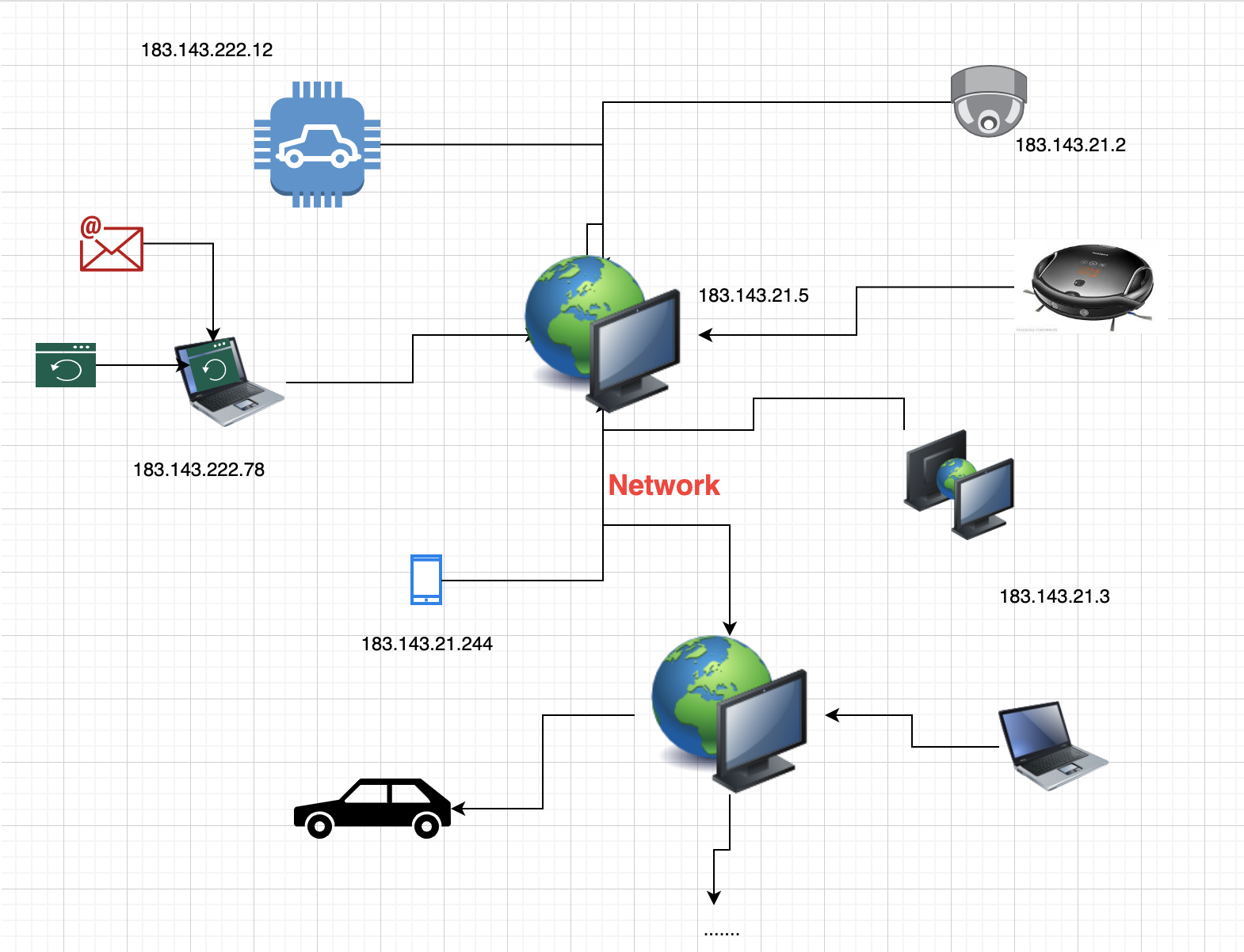
You can imagine the internet consists laptop, TV, cleaner robot, camera ip they are able to connect to internet.
Who was created the internet?
Vint Cerf - “father of the internet” and and his colleague Robert E. Kahn who co-designed the TCP/IP protocol and the architecture of the internet. In December 1997, President Bill Clinton presented the U.S nation medal of Technology
Who is control the internet?
No one owns the internet or controls who can connect to it. The internet is a network of networks. Each of the separate networks belongs to different companies and organizations, they rely on physical servers in different countries with varying laws and regulations.
Internet usage
The internet is the world most popular computer network. It began research in 1969 and became a global commercial network in the 1990s. Currently, there are early 5 billion people using the internet in the world and that number is still growing
Most people access internet using a web browser. It became so popular that many people consider internet and web synonymous. But in reality, the web is just one of many internet applications. In addition, there are many other popular applications.
Internet components

There are three basic components of the internet:
-
Client- which is the computer that connects with a remote computer or server to request information.
-
Server- which is the computer that provides service or shares resources to the client. This functionality of client and server work on a model called - call and response. It performs serveral tasks to provide the most relevant and accurate information for each request and fast execution time.
-
Protocol- which is a set of functions that need to be followed to find the desired data

The Protocols are crucial elements of the internet. It’s difined as a set of rules that guide the transmission of data beetwen computing devices. The rules make sure that the data request is sent and received by the client without any problem. There are two important protocols:
- Transmission Control Protocol(TCP)
- Internet Protocol (IP)
Each computer divice has a unique IP adress, it helps computers recognize each other more easily. The TCP/IP protocols make the data request and receiving possible between to computers via server.
How does the internet work?
How to transfer data from computer to another one?
Data is transmitted from one computer to another in the form of bits (10110101010010100100) through various media such as Ethernet cables, wireless signals (wifi-radio wares) and fiber optic cables
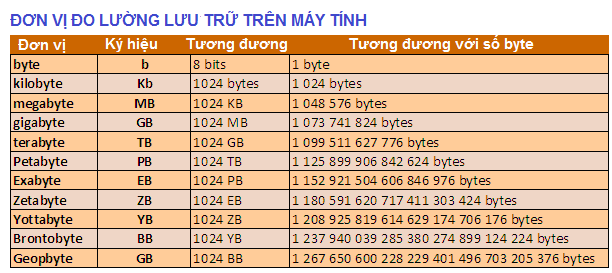
Bits and byte
-
Bits(binary digit) is the smallest unit used to represent information in a computer and is also used
to measure the transmission speed of information over a network. It is written binary (0 and 1). -
Bytes is the smallest data storage unit in a computer memory. 1 byte represents 256 stale value of information, 1 byte represent the number 0-255.
Internet transmission media (Ethernet cables ,fiber optic cables and wireless signal )
| METHOD | pro | Con |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity(Ethernet cables) | cheap | signal loss (short transmission) |
| Light(fiber optical cables) | really fast , no signal loss | expensive , hard to work with |
| Radio waves(wireless-wifi) | totally mobile | short range |
IP addresses
What is IP?
IP (Internet Protocol) is a digital address availble on a network-connected devices to share data with each other through internet connection protocols. Ex:127.0.2.1 , 192.142.23.2 ,…
What is IP used for?
Each divice connected to the net work has it owns IP address, you can think of it as a home or business address. IP will help divices on the internet be able to distinguish, share and communicate with each other.
Versions of the IP protocol.
-
IPv4(Internet protocol version 4) It is the fourth version of internet protocols.
-
IPv6(Internet protocol version 6)
DNS (Domain Name System)
What is DNS?

DNS (Domain Name Systym) invented in 1984 is a system that allows to establish correspondence between IP addresses and domain names on the Internet. Simply put, it is a system that helps convert numeric IP addresses (for example, 66.220.149.25) to domain names that are easy for humans to remember (for example, youtobe.com) and vice versa.
Uses
It serves the user as a “Phone Book”, capable of searching and translating domain names into IP addresses. It stores a huge amount of information and is tied to fixed IP addresses. Domain names are easier for users to remember than complex IP addresses.
Function
DNS can be understood as an “interpreter” and “communicator”. When opening a Web browser and entering the website name, the browser will go directly to the website without having to go through the IP address of the website. The DNS helps each other to translate “IP” addresses into “names” and vice versa. The user only needs to remember the “name”, no need to remember the IP address.
HTPP and HTML
HTPP
What is HTPP?

HTPPS(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) is an Http protocol that uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt data during data transmission, increasing the security of data transmission between Web server and Web browser.
How does HTPP work?
HTTP gives users a way to interact with web resources such as HTML files by transmitting hypertext messages between clients and servers. HTTP clients generally use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
HTML

WHat is HTML?
HTML (Hyprer Text Markup Language) is a standard markup language for creating web pages. It allows creating and structuring sections, paragraphs, and links using HTML elements. An HTML document is made of many HTML tags and each HTML tag contains different content.
An HTML document is formed by HTML elements (HTML Elements) specified by pairs of tags (tags and attributes). These tag pairs are enclosed by a curly brace (e.g. < html >) and are usually declared as a pair, consisting of an opening tag and a closing tag. Ex: (< p > and < /p > ).
WHO is the father of HTML?
 Tim Berners-Lee -The father of HTML also the founder of the World Wide Web and president of the
World Wide Web Consortium(W3C-organization that sets standards in the Internet environment).
HTML settings and structures are operated and developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Tim Berners-Lee -The father of HTML also the founder of the World Wide Web and president of the
World Wide Web Consortium(W3C-organization that sets standards in the Internet environment).
HTML settings and structures are operated and developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Structure of an HTML paragraph
Each HTML page contains a set of tags (also called elements).Each card will have certain effects, helping to build a complete structure for the Website.
You can think of it as the building blocks of a website. It forms a directory tree structure that includes sections, paragraphs, headings, and other content blocks.
Most HTML elements have an opening and closing tag with a structure like < tag >< /tag >.
Packets, Routing, and Reliability
Packets
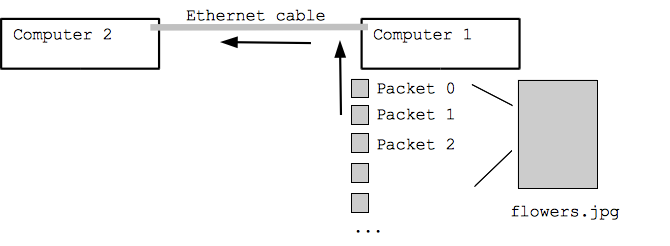 Packet is a term first coined by Donald Davies in 1965.
It is used to describe a segment of data that is sent from one computer or device to another
over a network.In simpler words, you can think of it as a packet full of data that is being
transferred to another region.
Packet is a term first coined by Donald Davies in 1965.
It is used to describe a segment of data that is sent from one computer or device to another
over a network.In simpler words, you can think of it as a packet full of data that is being
transferred to another region.
Packages divide data into more manageable “parts,” which move information more efficiently, and keep network resources from being constrained by a larger file.
A packet contains source, destination, data, size, and other useful information that helps
the packet to arrive at the proper location and reassemble properly.
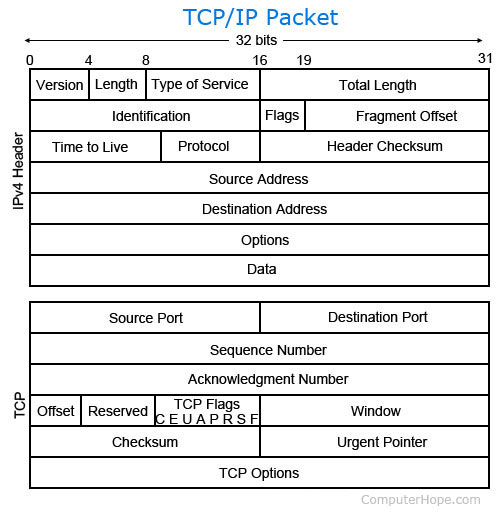
Routing
Router
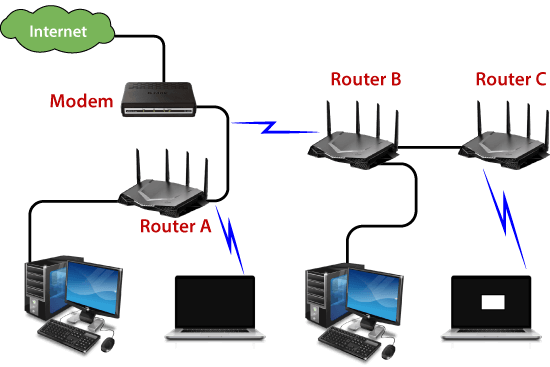
Router is a network device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Understandably, the router performs “direction of traffic” on the Internet.Data is sent on the Internet in the form of packets (Ex: email, web,…) , data packets will be forwarded from one router to another through small networks, which are connected to each other to form a network link, until the data packet reaches its destination.
In simple terms, routers connect devices in a network by transferring data packets between them. Routers perform this task by assigning a local IP address to each device on the network. This ensures that the data packet arrives at the right place and does not get lost in the network.
Routing
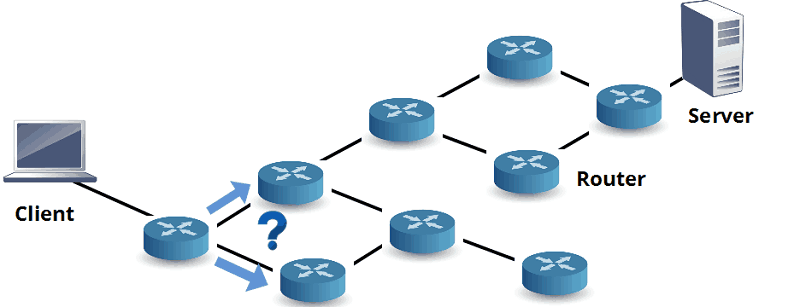
Routing is the method that a router or network device uses to deliver packets to the destination in the most optimal way, that is, to indicate the best direction and route for the packet. Routers collect and maintain routing information to enable transmission and reception of data.
Encryption and Public Keys
Encryption
What is Encryption
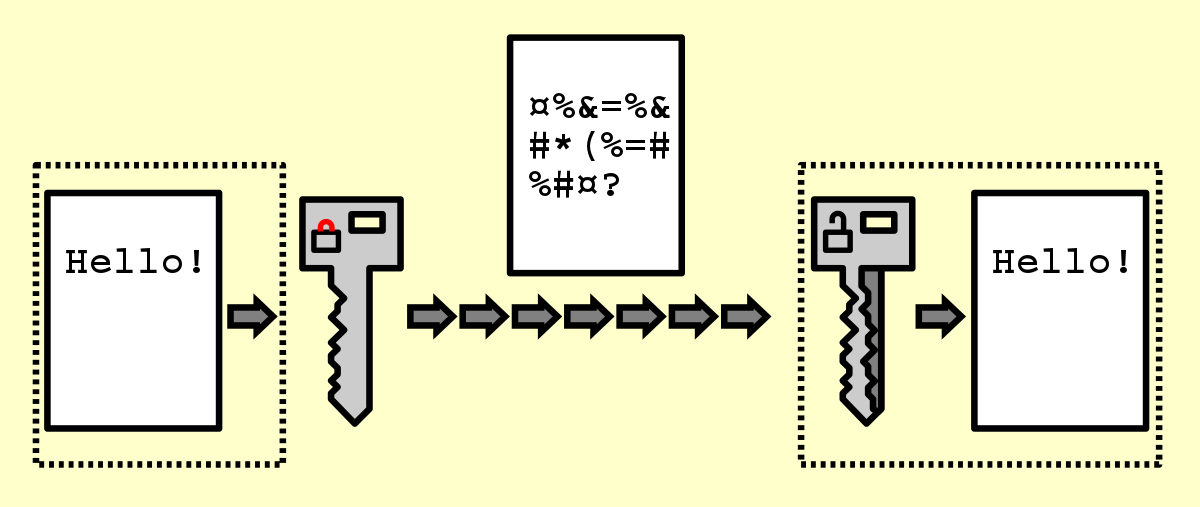
Encryption is the process of scrambling or enciphering data so it can be read only by someone with the means to return it to its original state. It is a crucial feature of a safe and trustworthy Internet. It helps provide data security for sensitive information.
Function
Encryption is commonly used to protect data stored on computer systems and data transmitted via computer networks, including the Internet. Financial transactions and private messaging communications often use encryption to increase security. Encryption is important when we need to find out whether data has been tampered with (data integrity), to increase people’s confidence that they are communicating with the people they think are communicating with (authentication) and to be sure that messages were sent and received (non-repudiation).
How Encryption Works ?
For data communicated over a network, encryption scrambles data using a secret value or key known only by the recipient and the sender. For stored data, the secret value is typically known only by the data owner.
Encryption Public Keys
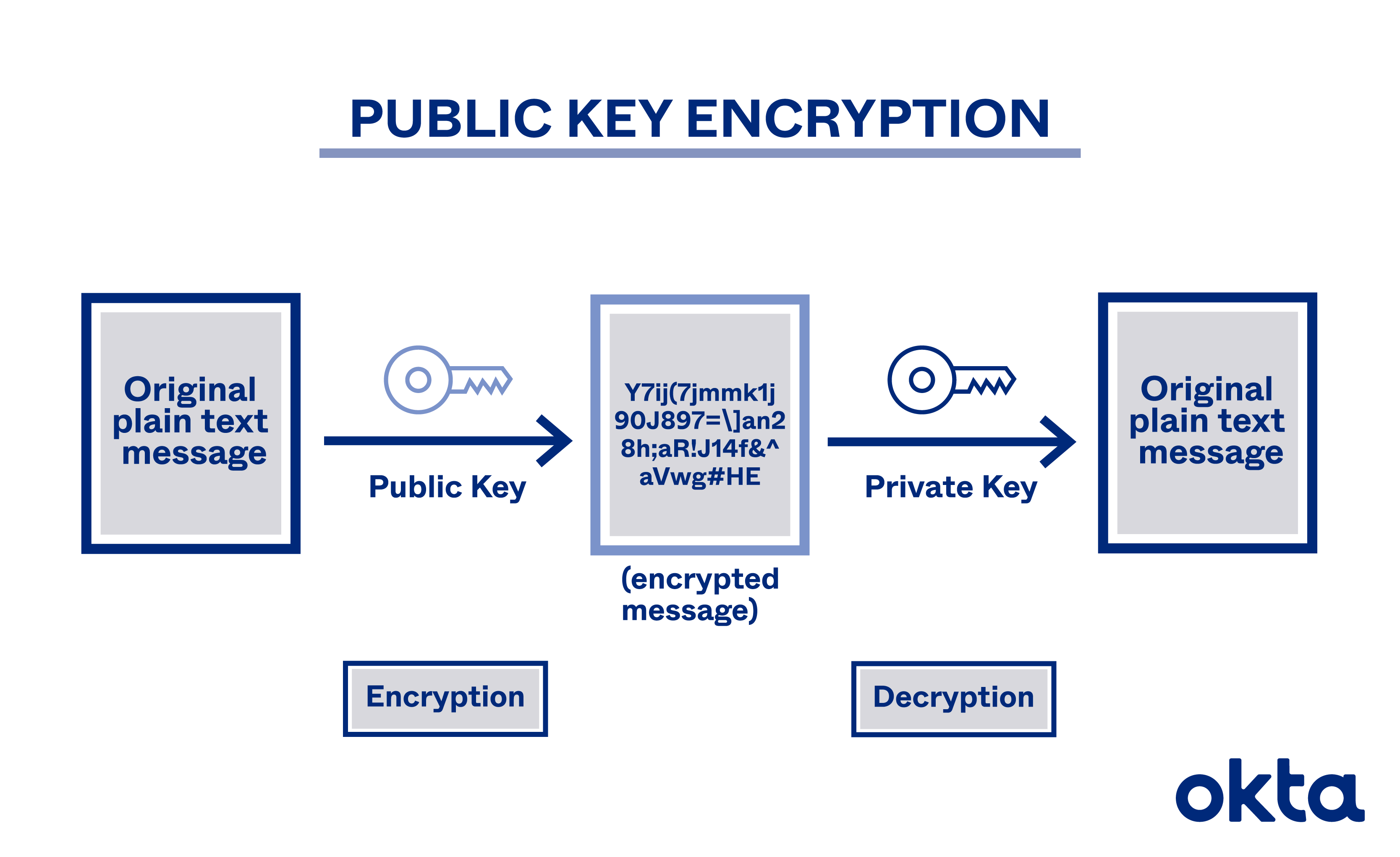
What is Encryption Public Key?
It is a method of encrypting data with 2 different keys, in which 1 key called Public Key is available for users to use and 1 key is Private Key. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa. Public key encryption also known as asymmetric encryption, is widely used for TLS/SSL(Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer).
Functions
Public key encryption is important because users can only decrypt encrypted data if they have the private key.
Either of the two keys, the public key and the private key, can be used for encryption with the key used for decryption.
In a public encryption system, public keys can be freely shared with users to encrypt data and verify digital signatures. Only the user who owns the private key can decrypt the encrypted data and create a digital signature.
Cybersecurity and Crime
Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting critical systems and sensitive information from digital attacks, also known as information technology (IT) security. Cybersecurity measures are designed to combat threats against networked systems and applications
Cybercrime

Cybercrime is a crime involving and using computers and the internet carried out against an individual or organization, possibly a government, for the purpose of harming someone physically or mentally.
Cybercrime can cause direct harm or indirect harm to whoever the victim is.
However, the largest threat of cybercrime is on the financial security of an individual as well as the government.
Cybercrime causes loss of billions of USD every year.